Nowadays, we talk a lot about the electric vehicle (EV) and so about the challenges, difficulties, solutions, etc. There is one great difference a driver experiences while comparing internal combustion engines (ICE) and electric vehicles (EV) is how they refuel. The fueling of a conventional vehicle is relatively uncomplicated (unless you refuel the wrong type of fuel) and this thing has become very comfortable for drivers over the years. As we are shifting towards electric mobility, adaptation to the new set of rules and terminologies are difficult. With so many terms (like AC and DC charging, different levels of charging, types of cables, types of plugs), it becomes more complicated to recognize each terminology and use.
As the EV market is booming, many of the industries, governments and other governing bodies adopting new technologies and terms which suit them thus it’s easy to get lost. This is increasing complexity.

One of the topics which EV drivers find quite confusing is around charging cables and plugs. The charging cables and charging stations and plugs comes in various shapes and sizes, they also differ according to the country you’re in, the type of vehicle you drive and the type of charging station you want to use. Due to these no of variables, selecting the right plug and cable for vehicle charging seems disconcerting – but it shouldn’t be.
Read on as we sorted out the differences between EV charging cables and plugs so you can charge confidently wherever you go.
Various Charging Cables for Charging an EV
Charging cables are an important part of charging an electric vehicle. The types of charging cables are called “Modes”. It is also confusing sometimes as the modes do not necessarily correlate to the charging levels. So on in this section, we will differentiate each model.
1. Mode 1 charging cables
Mode 1 charging cables are easy to recognize where you simply connect an EV to a standard AC socket and standard plug without a special safety system. Thus, there is no end to end communication between the vehicle and charging point. Mode 1 is used for charging electric bikes and electric scooters. This mode is prohibited in many countries across the world due to the unavailability of the safety system.
2. Mode 2 charging cables
Unlike Mode 1, this mode requires the safety system between the car in charge and the standard charging socket. The safety system is placed on charging cables and is called the Control box. This mode can be used for domestic and industrial sockets.
3. Mode 3 charging cables
This mode requires that a vehicle is charged through a power supply system permanently connected to the electrical network. This is the most common and used mode for charging at various commercial charging points, wall boxes and automatic charging systems.
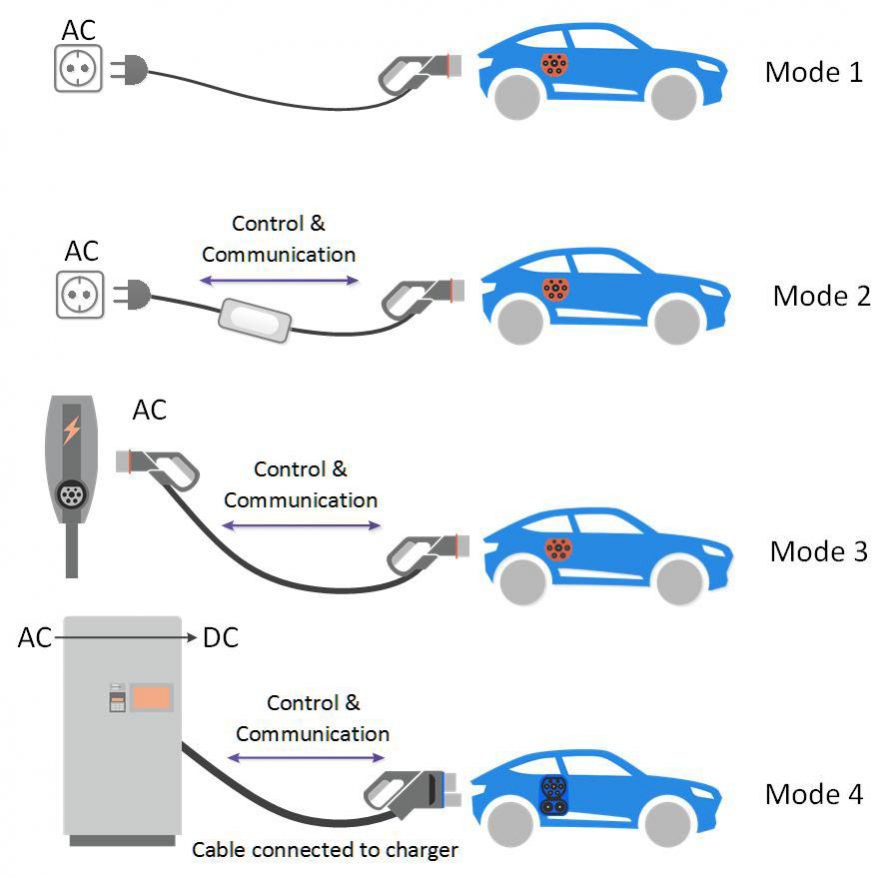
4. Mode 4 charging cables
All the above three modes provide Alternating Current. This charging mode is used for DC charging and the current is converted from AC to DC by a converter before it’s transferred to the vehicle.
What are the charging plugs for charging electric cars?
A charging plug is a connector that you put into the charging socket for charging an electric vehicle.
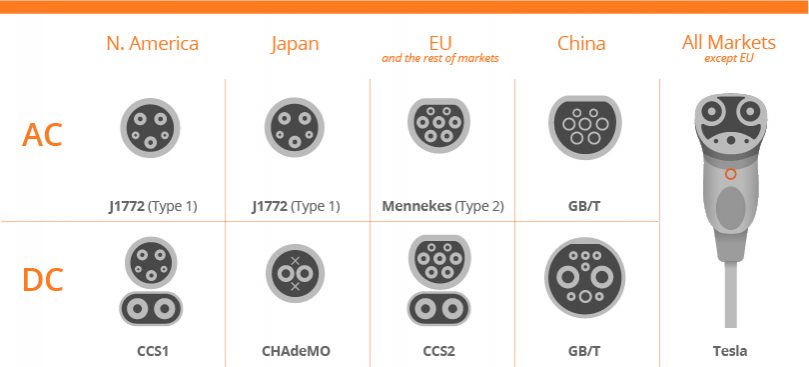
EV charging plugs types
- AC charging plugs
- Type 1 charging plug
Type 1 plug also referred to as SAE J1772. They are most commonly used with vehicle models found in Japan and North America. They are used as single-phase and they can deliver a power output of up to 7.4 kW.
- Type 2 charging plug
Type 2 plugs are designed by a German Company—also referred to as “Mennekes”. These are the official plug standard for the European Union. These three-phase plugs possess a higher power transfer capacity than Type 1 plugs.
- GB/T charging plug
China has developed their charging system called GB/T. There are two variations of GB/T plugs for AC charging and one for DC fast charging. The GB/T AC charging plug is single-phase and they can deliver up to 7.4 kW. It looks like the Type 2 plug, their receptors are reserved.
- DC charging plugs
- CCS charging plug
The fast-charging plug-in North America (CSS1) and Europe (CSS2) combine the J1772 connector with high speed charging pins.
CCS1
This is an enhanced version of the Type 1 AC plug. It has an additional two power contacts to enable DC fast charging with its plug. CCS1 is the widely used fast charging plug across North America after Tesla’s Supercharger technology.
CCS2
It is an enhanced version of the Type 2 AC plug with an additional two power contacts to enable DC fast charging. In this, AC charging is also supported by plugging a standard Type 1 (for CCS1) or Type 2 (for CCS2) plug into the upper half of the plug while it leave the lower DC power contacts empty in the plug (CSS2).
- CHAdeMO charging plug
It was developed in Japan enables fast charging of up to 200 kW as well as bidirectional charging. All DC fast chargers in Japan use a CHAdeMO connector. CHAdeMO connectors do not share part of the connector with the J1772 inlet, unlike the CCS system, due to which they require an additional CHAdeMO inlet on the car.
- Tesla charging plug
Tesla Charging Plug mostly uses the same connectors of level 1, level 2 and DC fast charge. It’s is a propriety connector by Tesla that accept all voltage results in no need of separate connector specifically for DC Charge. These stations are exclusive to Tesla Customers. Even you use an adapter cable; it would not be possible to charge non-Tesla EV at this station.