The Critical Role of EV Homologation
As the electric vehicle (EV) industry gains momentum, ensuring the safety, performance, and regulatory compliance of these vehicles becomes critical. This article explores EV compliance and EV homologation in the context of EVs. EV Compliance tests if a product meets predefined standards, while homologation provides approval for commercialization. Both are essential for consumer safety, innovation, and the EV industry’s growth. This article covers the basics of compliance, homologation, their standards, and their role in electric mobility.
1. Compliance and Homologation: Foundations of Assurance
1.1 Compliance: Testing for Conformity
In the EV landscape, compliance ensures products meet performance benchmarks. These tests determine if a product functions as expected and meets prescribed standard parameters. Compliance testing is straightforward: a product is either compliant or non-compliant based on test outcomes. There’s no room for ambiguity. Additionally, homologation standards for electric vehicles play a critical role in certifying that the products not only meet performance benchmarks but also adhere to a comprehensive set of regulatory and safety guidelines before they can enter the market.
For example, consider evaluating a drive shaft’s tensile strength. A standard defines the minimum strength required. If it falls below, the component fails the compliance test.
1.2 Homologation: Certifying Conformity
Homologation goes further, assessing products against a spectrum of standards. It’s the gateway to market entry, certifying compliance with norms. The process includes standardized tests aligned with Central Motor Vehicle Rules (CMVR) and emphasizes safety. Manufacturers typically start homologation after pre-compliance testing, minimizing iterative testing.
Homologation also involves meticulous documentation of testing procedures and outcomes, serving as a testament to regulatory compatibility.

2 Homologation Standards: Mapping the Path
2.1 Understanding the Nomenclature
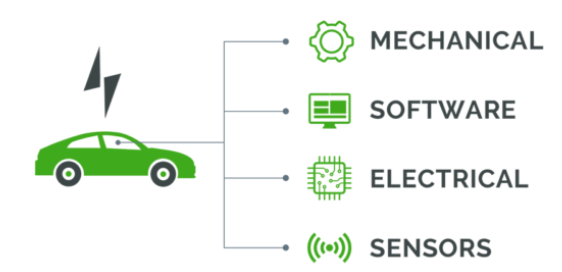
In EVs, standards are vital. AIS (Automotive Industry Standards) is the standardized nomenclature governing compliance and homologation. Each AIS relates to specific EV aspects, such as EV safety standards, efficiency, and performance.
For example, AIS-038 covers construction and functional safety standards, ensuring safe and efficient component placement. AIS-039 measures electrical energy consumption, while AIS-040 measures EV range. AIS-041, AIS-048, and AIS-049 respectively address net power measurement, battery safety, and type approval under CMVR.
2.2 Role of Homologation Standards
Homologation standards guide testing during the process. They provide precise criteria for assessment, ensuring uniformity, consistency, and comparability. These standards offer a clear path for manufacturers, regulators, and testing agencies, reducing ambiguity.
The Power of Assurance: Compliance and Homologation in Perspective
- Ensuring Quality and Safety:
Compliance and homologation ensure EV quality and safety. Compliance tests validate products’ adherence to performance benchmarks, ensuring roadworthiness. Homologation raises the bar, assessing conformity to multiple standards, guaranteeing efficient and safe EVs for consumers.
- Pioneering Innovation:
While setting stringent baselines, compliance and homologation also encourage innovation. These standards provide a framework for creativity within a regulated environment, driving technology, performance, and sustainability advancements.
- Driving Market Growth:
Electric Vehicle compliance and effective homologation accelerate market growth.. Manufacturers can confidently launch products, reducing development cycles and uncertainties. Standardized benchmarks build consumer confidence, boosting EV demand and market expansion.
- Fostering Global Consistency:
Global consistency is crucial for the EV industry. Compliance and homologation provide a common language, facilitating international trade. This harmonization ensures EVs navigate various regulatory landscapes while adhering to consistent benchmarks.
- Forging a Sustainable Future:
Electric Vehicle homologation and compliance and homologation contribute to EVs’ environmental sustainability. They encompass energy efficiency standards, emission regulations, and eco-friendly practices, ensuring that EV homologation helps reduce the industry’s carbon footprint and promotes sustainable transportation.
Conclusion
EV compliance and homologation are essential for a sustainable, efficient, and technologically advanced electric mobility landscape. They harmonize innovation, safety, and performance, shaping the EV industry’s trajectory. Embracing these processes contributes to a greener and smarter future. Through standardized benchmarks and meticulous evaluation, compliance and homologation drive electric vehicles towards a new era of mobility.