"The Impact of CAD and CAE on the Automotive Industry"
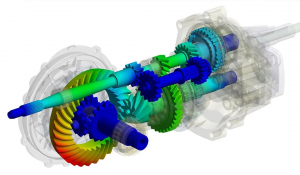
The automotive industry has always been on the cutting edge of innovation and technology, and the use of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) software has had a significant impact in recent years. Here are some examples of how CAD and CAE have changed the automotive industry:
Design process simplification:
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) software have had a significant impact on the automotive industry, particularly in streamlining the design process. Here are a few examples of how CAD and CAE have changed the design process in the automotive industry:
-
Faster design iterations: Automotive designers can use CAD software to quickly create and modify designs without having to start from scratch. This enables them to test different design concepts and iterate more quickly, resulting in a more efficient design process.
-
CAD software enables automotive designers to create accurate and precise 2D and 3D models of their designs, which can then be easily modified and refined. As a result, the final product is more accurately represented, reducing the need for physical prototypes and saving time and resources.
-
Collaboration and communication: CAD software enables automotive designers to collaborate on design projects from anywhere in the world. This improves communication and allows designers to more easily share ideas and feedback, resulting in a more cohesive design process.
-
CAE software allows automotive engineers to virtually simulate and test different design scenarios, reducing the need for physical prototypes. This saves time and resources while also allowing designers to spot potential design flaws earlier in the process.
-
Integration with manufacturing systems: CAD software can be integrated with manufacturing systems, allowing designers to create designs that are easily manufactured. As a result, the manufacturing process becomes more efficient, and the time and resources required to bring a product to market are reduced.
Enhancing product quality:
The automotive industry has benefited greatly from computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE) software by improving product quality. Here are some examples of how CAD and CAE have improved product quality in the automotive industry:
-
Virtual testing: CAE software allows automotive engineers to virtually simulate and test different design scenarios, allowing them to identify and correct potential design flaws before the product goes into production. This has resulted in a significant reduction in the number of product recalls and an overall improvement in the quality of automotive products.
-
Design optimization: Automotive designers can use CAD software to create accurate and precise 2D and 3D models of their designs, which can then be easily modified and refined. Designers can then optimise the design for functionality, performance, and safety, resulting in a higher-quality product.
-
Material selection: CAD software allows designers to simulate the behaviour of various materials and select the best material for the product. This ensures that the product is made of the best material possible, which improves its performance and durability.
-
Manufacturing efficiency: Because CAD software can be integrated with manufacturing systems, designers can create designs that are easily manufactured. As a result, the manufacturing process becomes more efficient, which reduces the likelihood of errors and improves product quality.
Standardisation: Automotive manufacturers can use CAD software to standardise their designs, ensuring that all products meet the same quality standards. This lowers the possibility of errors and raises the overall quality of automotive products.
Improving fuel efficiency and safety:
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) software have made significant contributions to the automotive industry’s fuel efficiency and safety. Here are some examples of how CAD and CAE have impacted the automotive industry in these areas:
-
Aerodynamics: CAD software enables designers to create precise 3D models that can be used to optimise a vehicle’s aerodynamics. Automobile manufacturers can reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency by improving airflow around the vehicle.
-
Lightweighting: Engineers can use CAE software to simulate the behaviour of various materials, allowing them to optimise the design for weight reduction while maintaining safety. Automobile manufacturers can improve fuel efficiency without sacrificing safety by reducing vehicle weight.
-
Crash testing: CAE software allows engineers to simulate a vehicle’s behaviour in various crash scenarios, allowing them to identify potential safety issues and make design changes prior to physical testing. This has resulted in significant advancements in vehicle safety.
-
Sensor integration: With CAD software, designers can create precise 3D models that can be used to integrate sensors into vehicle designs. As a result, safety features such as collision avoidance systems, lane departure warning systems, and backup cameras have seen significant improvements.
-
CAD software enables designers to create precise 3D models that can be used to optimise the placement and routing of electrical components. Automotive manufacturers can improve fuel efficiency by reducing the power required to run the vehicle’s electrical systems by optimising the electrical system.


Enabling faster prototyping:
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) software have had a significant impact on the automotive industry by enabling faster prototyping. Here are a few examples of how CAD and CAE have changed the prototyping process in the automotive industry:
-
Virtual prototyping: Automotive designers and engineers can use CAD and CAE software to create accurate and precise 2D and 3D models of their designs, which can then be easily modified and refined. This enables virtual prototyping, in which multiple design iterations can be created and tested quickly, resulting in a faster design process.
-
Rapid prototyping: 3D prototypes can be created using additive manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing using CAD and CAE software. This enables rapid prototyping, in which physical prototypes can be quickly and easily created, allowing designers to test and evaluate different design iterations more quickly.
-
CAE software allows engineers to virtually simulate the behaviour of various design scenarios, allowing them to identify potential design flaws and correct them before the product goes into production. This reduces the need for physical prototypes while also accelerating the prototyping process.
-
Collaboration: CAD and CAE software allow designers and engineers to work together and share designs and models in real time. This improves communication and accelerates the design process, allowing for quicker prototyping.
-
Iteration: CAD and CAE software enable rapid iteration of design concepts, allowing designers to quickly test and evaluate multiple design scenarios. This results in shorter design cycles and a faster prototyping process.
Reducing costs:
Cost-cutting software, such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE), has had a significant impact on the automotive industry. Here are some examples of how CAD and CAE have reduced costs in the automotive industry:
-
Improved design accuracy: CAD and CAE software allow designers and engineers to create highly accurate and precise designs, lowering the likelihood of errors and design flaws that can be costly to fix later in the product development process.
-
Reduced physical prototyping: Physical prototyping is reduced because CAD and CAE software allow designers and engineers to create accurate and precise 2D and 3D models of their designs, enabling virtual prototyping and simulation. This eliminates the need for physical prototypes, which can be costly to create and test.
-
Reduced time-to-market: CAD and CAE software allow designers and engineers to create designs more quickly and efficiently, reducing the time it takes to bring a product to market. This lowers development costs and allows automakers to respond to changing market conditions more quickly.
-
Reduced material waste: Engineers can use CAD and CAE software to simulate the behaviour of various materials and optimise the design for weight reduction, resulting in less material waste and lower material costs.
-
Collaboration: CAD and CAE software allow designers and engineers to collaborate and share their designs and models in real time, improving communication and reducing the need for costly physical prototypes and testing.

Conclusion
Overall, CAD and CAE software has transformed the automotive industry by allowing for faster, more efficient, and higher-quality product development. As technology advances, we can anticipate even more innovative and impactful applications in the automotive industry.


