Understanding EV Motors: Key Electric Vehicle Components
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the automotive industry, and at the heart of their performance lie critical electric vehicle components like motors and batteries.These factors determine an EV’s range, economy, and dependability in addition to how it operates. We’ll dissect these elements and their primary purposes in this post.
Choosing the right electric vehicle components is vital for energy efficiency and long-term sustainability.
Types of Motors
There are mainly two types of electric motors used in EVs:
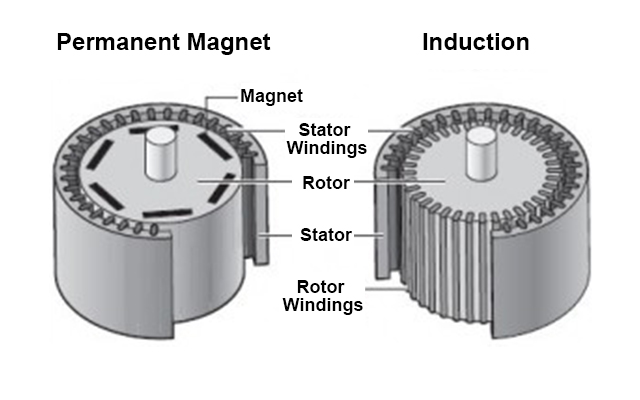
- AC Induction Motors: These are simple and reliable. They work by creating a magnetic field that spins to drive the wheels.
Diagram of EV motor types
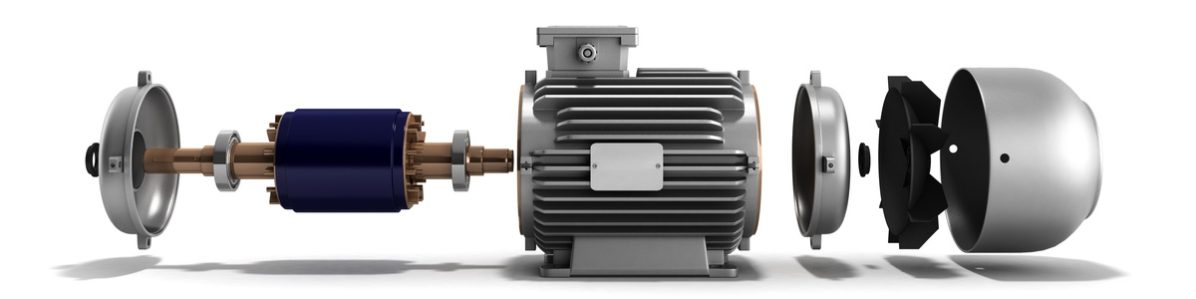
- Permanent Magnet Motors: These are more efficient and compact. They use strong magnets to generate motion.
How They Work?
When you press the accelerator in an EV, electricity flows from the battery to the motor. The motor then spins, transferring power to the wheels, which makes the car move forward.
Alternative Fuels Data Center – How Do All-Electric Cars Work?
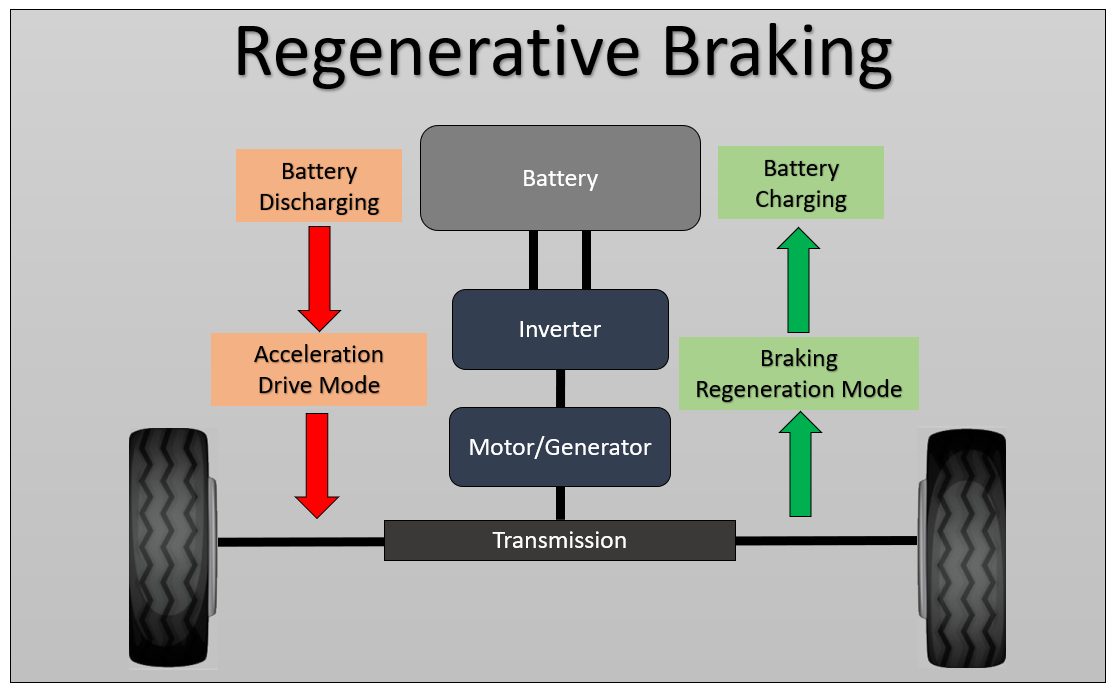
Regenerative Braking
This is a cool feature of electric motors. When you press the brake pedal,
the motor switches to a generator mode. Instead of wasting energy, it converts some of the kinetic energy from braking back into electricity, which goes back to the battery. This helps to recharge the battery a bit and improve the car’s overall efficiency.
Batteries: Storing Power for the Drive
Batteries in EVs are like giant rechargeable batteries you might use for your gadgets, but much bigger and more powerful. Here’s what you should know about them:
- Lithium-ion Batteries: Most EVs use lithium-ion batteries because they are lightweight and can store a lot of energy. These batteries power everything from the motor to the lights and air conditioning in the car.

- Types of Li-ion cells- Here are the names of different types of lithium-ion batteries:
Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2), Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4), Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (LiNiMnCoO2 or NMC), Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4), Lithium Titanate (Li4Ti5O12), Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminium Oxide (LiNiCoAlO2 or NCA), Lithium-Sulphur (Li-S).
- Battery Management System (BMS): To keep the battery safe and working well, EVs have a BMS. It monitors things like how much charge the battery has left, its temperature, and how fast it’s charging or discharging. This helps to make sure the battery lasts a long time and stays safe.
Why It Matters?
Understanding electric motors and batteries is important because they are at the core of how electric vehicles work. As technology improves, these components are getting better, allowing EVs to go farther on a single charge, charge faster, and become more affordable.
In the future, electric vehicles could play a big role in reducing pollution and using renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. By learning about these components now, you’re preparing to be part of a more sustainable and tech-savvy future.
So, the next time you see an electric car on the road, remember it’s not just about the cool design—it’s also about the amazing technology inside that makes it run. Who knows, maybe you’ll be designing the next generation of electric vehicles one day!
Electric motors and batteries are paving the way for cleaner, greener transportation, and understanding them gives you a peek into the exciting world of electric vehicles.
As technology evolves, the advancement of electric vehicle components will play a key role in shaping the future of mobility.